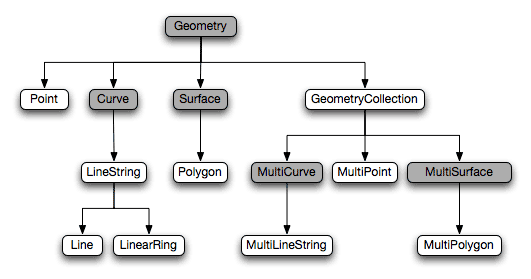
The Important Issues
Spatial data management is a critical component of geographic information systems (GIS) that involves the collection, storage, analysis, and dissemination of spatial data. Spatial data, also known as geospatial data, refers to information related to the location and shape of physical features on the Earth's surface. Effective management of this data is essential for a wide range of applications, including urban planning, environmental monitoring, transportation, and disaster management.
The process begins with data acquisition, which involves gathering spatial information from various sources such as satellite imagery, aerial photography, GPS devices, and existing maps. Once collected, the data must be stored in a structured manner using spatial databases that support spatial queries and spatial indexing. These databases enable efficient retrieval and manipulation of large volumes of geospatial data.
Data quality assurance is vital to ensure accuracy, completeness, and consistency of the data. Techniques such as data validation, cleaning, and standardization are employed to maintain high data quality. Additionally, metadata management plays a crucial role by providing information about the data’s origin, accuracy, and appropriate uses.
Analysis and modeling are key stages in spatial data management. GIS tools allow users to perform spatial analysis, such as overlay operations, network analysis, and terrain modeling, to extract meaningful insights. Visualization through maps and 3D models enhances understanding and supports decision-making processes.
Data sharing and dissemination involve establishing protocols and standards to facilitate the exchange of spatial information among different organizations and stakeholders. Web-based GIS platforms and open data initiatives are increasingly popular, promoting transparency and collaboration.
Challenges in spatial data management include dealing with large data volumes, ensuring data security and privacy, and integrating data from diverse sources with varying formats and qualities. Technological advancements, such as cloud computing, machine learning, and improved spatial databases, continue to address these challenges and improve the efficiency and capabilities of spatial data management.
In conclusion, spatial data management is a vital discipline that underpins geospatial applications impacting numerous sectors. Its effective implementation ensures accurate, timely, and accessible spatial information, enabling informed decision-making and sustainable development. As technology evolves, so will the methods and tools for managing spatial data, further enhancing its role in solving complex real-world problems.